Innovative Applications of Shift Register ICs in IoT Devices
Introduction
Over the decades, shift register integrated circuits (ICs) have found uses in applications like seven-segment displays, serial-to-parallel conversion, and more. With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), these versatile ICs are seeing creative new roles that leverage their unique digital timing and data transfer capabilities. This article explores how shift registers are enabling simpler, more integrated solutions across fields like image sensors, displays, remote systems, and more within the world of connected devices.
What Is a Shift Register?
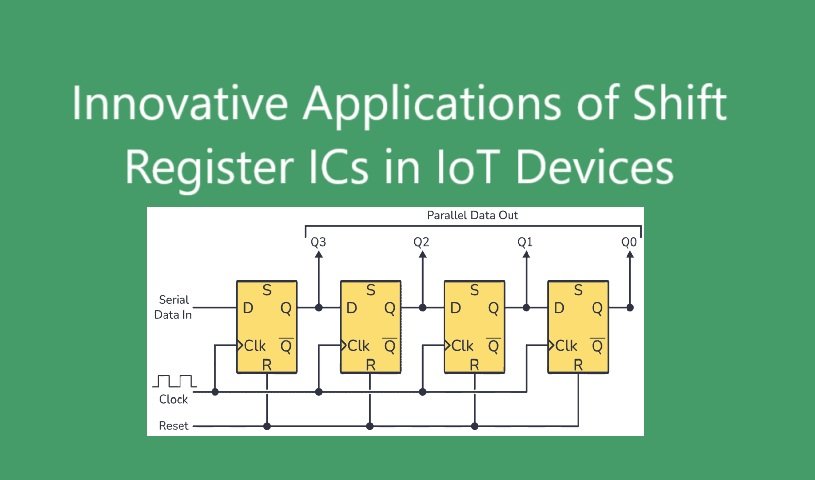
At its core, a shift register is a type of digital IC that stores discrete voltage levels representing binary data (1s and 0s) within a series of internal flip-flops. In response to clock pulses, it sequentially shifts the contents of each flip-flop into the next stage in the chain.
Basic Configurations:
- Serial-In, Serial-Out (SISO): A single bit enters the serial input pin during each clock cycle and exits as a bit stream from the serial output pin.
- Serial-In, Parallel-Out (SIPO): Data enters serially but can be read out simultaneously from parallel output pins.
- Parallel-In, Serial-Out (PISO): Parallel data loads into the register and shifts out serially.
- Bidirectional Shift Registers: These allow shifting data in either direction, increasing flexibility.
These properties make shift registers invaluable for applications involving digital timing, signaling, display driving, and more.
Image Sensing and Vision Processing
Shift registers have become critical components in digital image sensing for IoT devices such as cameras, biometric scanners, and machine vision systems. Let’s explore their roles:
CMOS Image Sensor Column-Parallel ADC Interface
In CMOS image sensors, column-parallel ADCs digitize pixel output voltages. Each pixel column shares a single ADC located at the end of the column. Shift registers sequentially select pixel voltages and feed them into the ADC for digitization. This efficient pipeline minimizes the number of ADCs needed, reducing costs and power consumption.
Environmental Monitoring Modules
Some IoT devices integrate digital imaging with environmental sensors. A shift register handles clocking pixel data out of the image sensor while controlling pulses to LED illumination and sequencing readings from humidity, temperature, and motion sensors. This integration simplifies microcontroller tasks and improves efficiency.
Fingerprint Sensing for Authentication
In optical fingerprint sensors, shift registers enable parallel loading of pixel data from the imaging array. The data then shifts out serially for processing by an authentication algorithm. This approach maximizes throughput and ensures secure, real-time operation.
Keypad and Display Multiplexing
Multiplexing with shift registers remains a popular technique for driving segmented displays and sensing input matrices. For example:
- Smart Thermostats: A shift register sequentially enables rows of an LCD and scans keypad inputs, reducing the number of required microcontroller pins.
- Wi-Fi Door Locks: Numeric keypads in door locks utilize shift registers to scan inputs and report them sequentially to a central processor.
Inventory Tagging and Asset Tracking
Shift registers play a role in reducing component counts in electronic tags used for inventory and asset tracking:
- Passive RFID Tags: A shift register clocks out stored ID data to modulate the tag’s antenna impedance.
- Active Bluetooth/WiFi Tags: Low-power tags use shift registers to control transmission intervals, conserving energy while maintaining functionality.
Automated Test and Calibration
In automated production and calibration systems, shift registers handle precise timing and distributed I/O tasks:
- Semiconductor Testing: Distributed shift registers control multiplexers and function generators in synchronized probing systems.
- Calibration Stations: Shift registers coordinate DACs and sensors for efficient, synchronized calibration in industrial environments.
Remote Control and Automation Systems
Shift registers enable distributed logic across automation systems:
- Building Energy Management: Shift registers in relay modules control lighting and HVAC systems over RS-485 backbones.
- LED Lighting Strips: Addressable shift registers drive long lighting arrays with minimal wiring.
Data Buffering and Fan-Out
Shift registers excel in data buffering and expanding I/O capabilities:
- LCD Displays: Shift registers buffer display data for smooth refresh cycles.
- Traffic Signals: Shift registers expand microcontroller outputs to control multiple signal arrays efficiently.
Application Convergence and Emerging Uses
Shift registers are increasingly used in convergent applications that integrate multiple functions:
- Integrated IoT Sensors: Combining imaging, environmental sensing, and communication in a single module.
- Biometric Security: Miniaturized fingerprint sensors with on-chip processing leverage shift registers for efficient data transfer.
- Distributed Robotics: Coordinating sensors and actuators in robotic systems using synchronized shift register arrays.
Latest Shift Register ICs
Modern shift register ICs offer enhanced features for IoT applications:
- 74HC595: Widely used for LED driving and data storage, with low propagation delay.
- 74HC165: Ideal for parallel-to-serial conversion in data gathering applications.
- MAX7219: Integrated for driving seven-segment LED displays with minimal external components.
- 74VHC164/165: High-performance, low-power shift registers for efficient data transmission.
Conclusion
Shift registers continue to play a crucial role in IoT device design, offering cost-effective and efficient solutions for digital timing, data transfer, and resource sharing. Their versatility ensures they remain relevant as technology evolves, supporting applications from imaging and biometrics to automation and beyond.