Everything You Need to Know about FR-4 PCBs
FR-4 is a type of flame-retardant fiberglass material that is widely used in the electronics industry. In this blog post, we will explore everything you need to know about FR-4 PCBs, including their composition, properties, advantages, and applications.
What is FR4?
FR4 is a type of material that is commonly used in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs). It is a composite material made up of layers of fiberglass cloth and epoxy resin. FR4 is known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, high mechanical strength, and flame retardant properties.
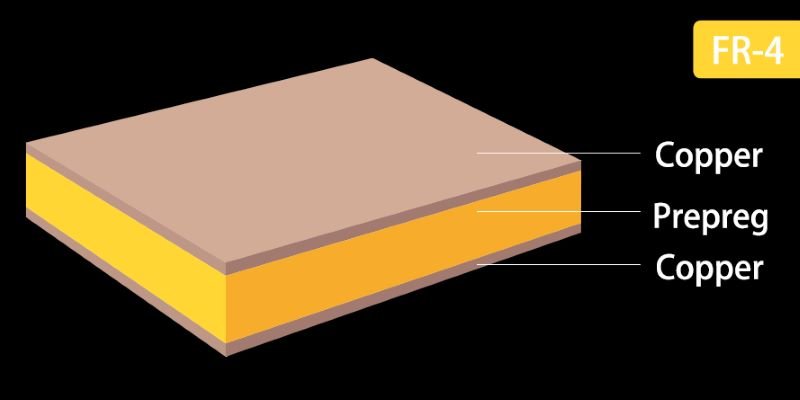
The term “FR4” stands for Flame Retardant 4, which refers to the material’s ability to resist catching fire and to self-extinguish if it does catch fire. This makes FR4 a safe and reliable choice for applications that require high levels of safety, such as in the aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries.
Types of FR4
There are different types of FR4 materials available, each with its own unique characteristics. Let’s take a look at some of the common types of FR4:
Standard FR4
Standard FR4 is the most commonly used type of FR4 material. It is known for its high electrical insulation properties, good thermal stability, and mechanical strength. Standard FR4 is suitable for a wide range of applications and is widely used in consumer electronics, automotive, aerospace, and telecommunications industries.
High-Temperature FR4
High-temperature FR4 is designed to withstand elevated temperatures without compromising its electrical and mechanical properties. It has a higher glass transition temperature (Tg) compared to standard FR4, making it suitable for applications that require operation at high temperatures, such as automotive engine control modules and industrial equipment.
Halogen-Free FR4
Halogen-free FR4 is an environmentally friendly alternative to standard FR4. It is manufactured without the use of halogenated flame retardants, which are known to release toxic gases when burned. Halogen-free FR4 offers the same electrical and mechanical properties as standard FR4 but with the added benefit of being more environmentally friendly.
Composition of FR-4 PCBs
FR-4 PCBs are made up of multiple layers of copper traces and a substrate material called FR-4. The substrate is a composite material composed of a woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with an epoxy resin. This combination of materials provides excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength to the PCB.
The copper traces on the FR-4 PCB are etched to create the desired circuit pattern. These traces act as conductive pathways for the flow of electrical current between different components on the board.
Properties of FR-4 PCBs
FR-4 PCBs offer several key properties that make them highly desirable for electronic applications:
- Flame Retardant: As the name suggests, FR-4 PCBs have excellent flame-retardant properties. This means that they are resistant to catching fire and can help prevent the spread of flames in case of a fire.
- High Temperature Resistance: FR-4 PCBs can withstand high temperatures without losing their structural integrity. This makes them suitable for applications where heat dissipation is a concern.
- Good Electrical Insulation: The fiberglass substrate of FR-4 PCBs provides excellent electrical insulation, preventing short circuits and ensuring reliable performance.
- Mechanical Strength: FR-4 PCBs have good mechanical strength, making them durable and resistant to physical stress and impact.
Advantages of FR-4 PCBs
FR-4 PCBs offer several advantages over other types of PCB materials:
- Cost-effective: FR-4 is a relatively inexpensive material, making FR-4 PCBs a cost-effective choice for many electronic applications.
- Widely Available: FR-4 PCBs are readily available in the market, making them easy to source for manufacturers.
- Excellent Electrical Performance: FR-4 PCBs have low dielectric loss and good signal integrity, ensuring reliable electrical performance.
- Compatibility: FR-4 PCBs are compatible with various assembly techniques, including through-hole and surface mount technologies, making them versatile for different manufacturing processes.
Applications of FR-4 PCBs
FR-4 PCBs find applications in a wide range of electronic devices and industries:
- Consumer Electronics: FR-4 PCBs are extensively used in consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and televisions.
- Industrial Equipment: FR-4 PCBs are commonly found in industrial equipment, including control systems, automation devices, and power distribution systems.
- Automotive Electronics: FR-4 PCBs are used in various automotive applications, including engine control units, dashboard electronics, and entertainment systems.
- Telecommunications: FR-4 PCBs are essential components in telecommunications equipment, such as routers, switches, and base stations.
The Benefits of FR4 in PCBs
FR4 is the material of choice for PCBs due to its numerous benefits. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of using FR4 in PCB manufacturing:
1. Excellent Electrical Insulation
One of the primary benefits of FR4 is its excellent electrical insulation properties. It has a high dielectric strength, which allows it to withstand high voltages without conducting electricity. This makes FR4 ideal for applications that require reliable insulation, such as power supplies, control systems, and electronic devices.
2. Mechanical Strength
FR4 is known for its exceptional mechanical strength. It has a high tensile strength, which enables it to withstand mechanical stress and vibrations. This makes FR4 suitable for applications that require durability and reliability, such as automotive and aerospace electronics.
3. Thermal Stability
FR4 has excellent thermal stability, meaning it can withstand high temperatures without losing its electrical and mechanical properties. This makes it suitable for applications that generate heat, such as power electronics and LED lighting systems.
4. Cost-Effectiveness
FR4 is a cost-effective material compared to other alternatives. It offers a balance between performance and affordability, making it a popular choice for PCB manufacturers. The availability of different types of FR4 materials allows manufacturers to choose the most suitable option based on their specific requirements and budget.
5. Compatibility
FR4 is compatible with a wide range of manufacturing processes, including drilling, etching, and soldering. This makes it easy to work with and allows for efficient PCB production. It also enables compatibility with various components and connectors, making FR4 a versatile choice for different applications.
Applications of FR4
FR4 is widely used in various industries and applications due to its excellent properties. Some common applications of FR4 include:
- Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): FR4 is the most commonly used material for manufacturing PCBs. It provides the necessary insulation and mechanical support for the components on the board, allowing for the proper functioning of electronic devices.
- Aerospace and Defense: FR4 is used in the aerospace and defense industries for applications such as avionics, radar systems, and missile guidance systems. Its high mechanical strength and flame retardant properties make it suitable for use in these critical and safety-sensitive applications.
- Automotive: FR4 is used in automotive electronics, including engine control units (ECUs), infotainment systems, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Its electrical insulation properties and ability to withstand harsh operating conditions make it ideal for use in the automotive industry.
- Consumer Electronics: FR4 is used in a wide range of consumer electronic devices, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and televisions. Its electrical insulation properties and flame retardant properties make it a safe and reliable choice for these applications.
- Industrial Equipment: FR4 is used in various industrial equipment, such as power supplies, control systems, and industrial automation systems. Its high mechanical strength and chemical resistance make it suitable for use in demanding industrial environments.
Choosing the Right FR4 Thickness
Now that you understand the factors to consider let’s discuss how to choose the right FR4 thickness for your PCB:
1. Determine the Application
Start by determining the specific application of your PCB. Will it be used in a high-frequency circuit, power electronics, or general-purpose applications? Understanding the intended use will help you prioritize the necessary electrical and mechanical properties.
2. Consult Design Guidelines
Check the design guidelines provided by your PCB manufacturer or consult with their technical support team. They will often have recommendations and specifications for the appropriate FR4 thickness based on the intended application and the number of layers in your design.
3. Consider Signal Integrity
If your PCB design involves high-speed signals or RF circuits, signal integrity is crucial. Thinner FR4 laminates with lower dielectric constant and controlled impedance characteristics are typically preferred for such applications to minimize signal loss and distortion.
4. Evaluate Mechanical Requirements
Evaluate the mechanical requirements of your PCB, such as the expected mechanical stress, weight limitations, and mounting constraints. Thicker FR4 laminates offer better mechanical strength and rigidity, making them suitable for applications that require high durability.
5. Budget Constraints
Consider your budget constraints when selecting the FR4 thickness. Thicker FR4 laminates are generally more expensive, so it is essential to find a balance between the desired performance and the available budget.
Exploring Alternative PCB Materials: Beyond FR4
1. Polyimide (PI)
Polyimide, also known as PI, is a popular alternative to FR4 for PCB manufacturing. It is a high-temperature resistant material that can withstand extreme temperatures without losing its electrical and mechanical properties. This makes it suitable for applications that require PCBs to operate in harsh environments, such as aerospace and automotive industries. Additionally, PI has excellent chemical resistance and low outgassing properties, making it ideal for applications that involve exposure to chemicals or vacuum environments.
2. Rogers Corporation Materials
Rogers Corporation offers a range of high-performance PCB materials that are alternatives to FR4. These materials, such as RO4000 series and RO3000 series, are designed to provide superior electrical performance, low loss, and high frequency capabilities. They are commonly used in applications that require high-speed signal transmission, such as telecommunications, wireless communication, and radar systems. Rogers Corporation materials are known for their low dielectric constant and low dissipation factor, which contribute to improved signal integrity.
3. Metal Core PCBs
Metal Core PCBs, also known as MCPCBs, are another alternative to FR4. As the name suggests, these PCBs have a metal core, typically made of aluminum or copper, instead of a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate. The metal core provides better heat dissipation, making MCPCBs suitable for applications that involve high power and require efficient thermal management. They are commonly used in LED lighting, power electronics, and automotive applications.
4. Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs, also known as Flex PCBs, offer a unique alternative to traditional rigid PCBs made of FR4. These PCBs are made of flexible substrates, such as polyimide or polyester, which allow them to bend, twist, and fold. Flexible PCBs are ideal for applications that require compact and lightweight designs, as well as the ability to conform to irregular shapes. They are commonly used in wearable devices, medical equipment, and automotive electronics.
5. Ceramic PCBs
Ceramic PCBs are a specialized alternative to FR4 that offer excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties. These PCBs are made of ceramic materials, such as aluminum oxide (Al2O3) or aluminum nitride (AlN), which have high thermal conductivity values. Ceramic PCBs are commonly used in power electronics, high-power LED lighting, and RF/microwave applications. The high thermal conductivity of ceramic PCBs allows for efficient heat dissipation, while their electrical insulation properties ensure reliable performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, FR4 is a versatile and reliable material that is widely used in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards. Its excellent electrical insulation properties, high mechanical strength, and flame retardant properties make it a popular choice for applications that require high levels of safety and reliability. Whether it’s in the aerospace, automotive, or electronics industry, FR4 plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning of electronic devices and systems.