Active and Passive Components: Definitions, Applications and Differences
Electronic components are the building blocks of all electronic devices. They are broadly classified into two categories: active and passive components. Understanding the difference between these two is crucial for designing efficient circuits and devices. Active components, like transistors, are capable of amplifying signals and require an external power source to operate, while passive components, such as resistors and capacitors, do not amplify signals but play a vital role in energy storage, filtering, and signal conditioning. This article explores the definitions, examples, and roles of active and passive components, along with a comparison of their key differences.
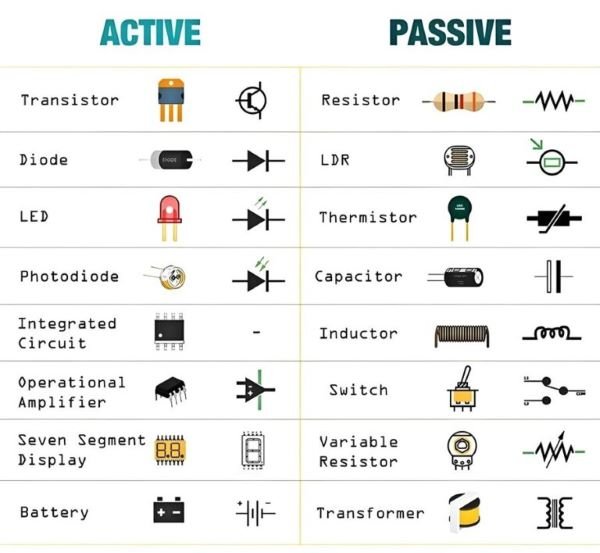
What are Active Electronic Components?
Active electronic components are devices that can control the flow of electricity and are capable of amplifying or switching electronic signals. These components require an external power source to function and can inject energy into a circuit, making them essential for signal processing and amplification in electronic systems.
Examples of Active Components
- Transistors: Semiconductors that can amplify electrical signals or act as electronic switches.
- Diodes: Devices that allow current to flow in one direction, commonly used for rectification.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): Complex assemblies of transistors, diodes, and other components integrated into a small chip, used for signal processing, computing, and control functions.
- Operational Amplifiers: ICs used for signal amplification, filtering, and mathematical operations.
Role of Active Components in Circuits
Active components are essential for controlling and amplifying electronic signals in a circuit. They are commonly used in power supplies, amplifiers, and oscillators. For instance, transistors can switch electronic signals on and off, while operational amplifiers are used to increase the magnitude of a weak signal. These components are vital for signal generation, amplification, and control functions, enabling the creation of complex and dynamic electronic systems.
What are Passive Electronic Components?
Passive electronic components are devices that do not require an external power source to operate and cannot amplify electrical signals. Instead, they store, dissipate, or filter energy within an electronic circuit. Passive components are vital for controlling voltage, current, and frequency in circuits.
Examples of Passive Components
- Resistors: Components that resist the flow of electrical current, used to control voltage and current levels.
- Capacitors: Devices that store electrical energy in an electric field, commonly used for filtering, energy storage, and signal coupling.
- Inductors: Components that store energy in a magnetic field when current flows through them, used for filtering and energy storage in power supplies.
- Transformers: Devices that transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction, typically used for voltage conversion.
Role of Passive Components in Circuits
Passive components play crucial roles in energy management, signal conditioning, and circuit protection. For example, resistors are used to control current and protect components from overcurrent, while capacitors and inductors are often employed in filter circuits to remove unwanted noise or stabilize voltage. These components do not generate or amplify signals but are essential for maintaining proper circuit function and stability.
Key Differences Between Active and Passive Components
Energy Source Requirement
- Active Components: Require an external power source to operate. This allows them to control electrical signals and inject energy into the circuit. For instance, transistors need a separate power supply to amplify signals.
- Passive Components: Do not need any external power source. They either store or dissipate energy but cannot introduce energy into the circuit. Resistors, for example, simply resist current without needing a power supply.
Amplification Capabilities
- Active Components: Have the ability to amplify signals. This means they can increase the strength of an input signal. Transistors, for instance, can take a small input signal and generate a larger output.
- Passive Components: Cannot amplify signals. They may affect the current or voltage in a circuit but only reduce or store energy, rather than increasing signal strength.
Direction of Current Flow
- Active Components: Can control the direction of current flow and can switch current on or off. Diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, while transistors can completely block or allow current.
- Passive Components: Typically do not control the direction of current flow. They allow current to pass through in either direction (except for some like inductors, which may resist changes in current direction).
Role in Energy Storage or Dissipation
- Active Components: Primarily involved in the control and amplification of energy, rather than storage or dissipation. They manage energy flow and adjust how circuits behave under certain conditions.
- Passive Components: Play a significant role in storing and dissipating energy. Capacitors store energy in an electric field, and resistors dissipate energy as heat.
Examples of Circuits Utilizing Both Types
Many practical electronic circuits incorporate both active and passive components to perform their functions. For example:
- In a power supply circuit, diodes (active components) rectify the AC voltage, while capacitors (passive components) filter the output to provide a smooth DC signal.
- In an amplifier circuit, transistors (active) amplify the signal, while resistors and capacitors (passive) help in signal conditioning and feedback control.
Applications of Active Components
Use in Amplification, Switching, and Signal Modulation
Active components are integral to modern electronics for their ability to amplify signals, switch electrical currents, and modulate signals. They play crucial roles in:
- Amplification: Transistors and operational amplifiers boost weak signals, which is essential in devices such as audio amplifiers and radios.
- Switching: Transistors are also used as electronic switches, enabling digital logic circuits, microcontrollers, and power regulation in devices like computers and smartphones.
- Signal Modulation: Active components like transistors and diodes are used in communication systems to modulate signals, allowing for the transmission and reception of data in wireless communication, radio, and TV systems.
Examples of Real-World Applications
- Microprocessors and Computers: Integrated circuits, which consist of numerous transistors, form the core of CPUs, enabling complex data processing and computations.
- Communication Devices: Diodes and transistors are used in radios, telecommunication systems, and mobile phones for signal modulation and amplification.
- Power Supplies: In switching power supplies, active components control and regulate the output voltage to power various electronic devices efficiently.
Applications of Passive Components
Use in Energy Storage, Filtering, and Voltage Regulation
Passive components are essential in managing and stabilizing energy flow in electronic circuits. They are widely used for:
- Energy Storage: Capacitors store electrical energy temporarily and release it when needed, while inductors store energy in magnetic fields.
- Filtering: Capacitors and inductors are used to filter unwanted signals or noise in electronic circuits, particularly in power supplies and audio equipment.
- Voltage Regulation: Resistors help control the flow of current and regulate voltage levels across components, preventing damage and ensuring stable operation in circuits.
Examples of Real-World Applications
- Power Supply Circuits: Capacitors are used to smooth out fluctuations in power supplies, while resistors help maintain voltage levels.
- Audio Systems: Inductors and capacitors are used in speaker crossovers to separate different frequency ranges, improving sound quality.
- Signal Filtering: Passive filters are used in communication devices to remove noise and improve signal clarity.
Importance of Using Both in Electronic Circuit Design
How Active and Passive Components Complement Each Other
In electronic circuits, active and passive components work together to achieve desired functions. Active components, such as transistors and diodes, rely on the passive components, like resistors and capacitors, for supporting roles like signal filtering, voltage regulation, and energy storage. For example, a transistor amplifier circuit depends on resistors and capacitors for proper biasing and signal conditioning.
Designing Efficient Circuits with Both Types
By combining the capabilities of active components (amplification, switching) with the stability and filtering functions of passive components, engineers can design efficient and reliable circuits. In a typical power supply, for example, diodes (active) rectify AC to DC, while capacitors (passive) smooth out the output to ensure a steady DC voltage. Similarly, in audio systems, active amplifiers work in conjunction with passive filters to deliver clear and amplified sound.
Conclusion
In summary, both active and passive electronic components are essential in modern circuit design. Active components, such as transistors and diodes, provide the necessary control and amplification, while passive components, like resistors, capacitors, and inductors, manage energy flow and signal conditioning. Understanding the differences and complementary roles of these components is crucial for designing effective electronic devices. By using both types of components, engineers can create sophisticated and efficient circuits that power everything from simple household devices to complex communication systems.