How to Choose Right Surface Finish For Your PCB
Introduction
When it comes to designing and manufacturing a printed circuit board (PCB), one crucial aspect that often gets overlooked is the choice of surface finish. The surface finish plays an important role in protecting the copper traces and ensuring the reliability and functionality of the PCB. With numerous options available, it can be challenging to determine the right surface finish for your specific application. In this article, we will guide you through the process of choosing the ideal surface finish for your PCB.
Evaluating the Different Surface Finish Options
There are several surface finish options available in the market, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most commonly used surface finishes:
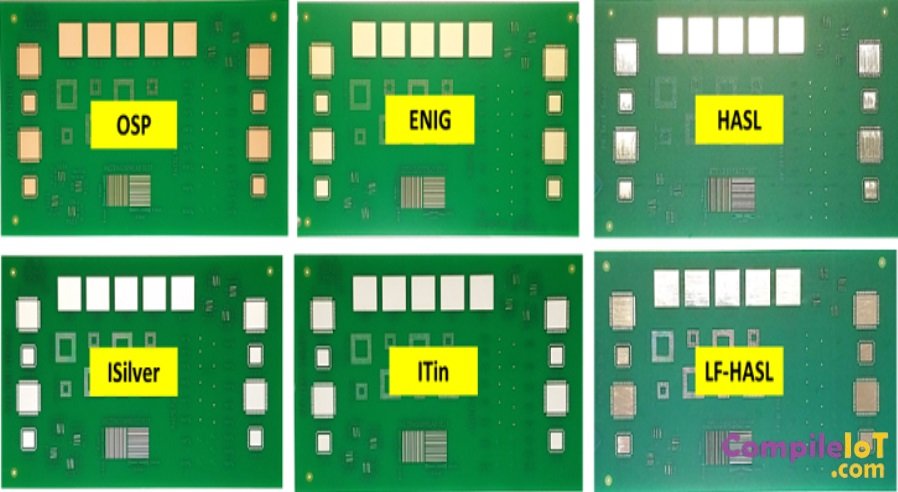
1. HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling)
HASL, also known as solder leveling, is one of the oldest and most widely used surface finishes. It involves coating the entire PCB with a layer of solder and then leveling it using hot air. HASL provides excellent solderability and is relatively cost-effective. However, it is not suitable for fine-pitch components due to its uneven surface and potential for solder bridging.
2. ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold)
ENIG is a popular surface finish in the PCB industry, especially for high-reliability applications. It consists of a thin layer of nickel followed by a layer of gold. ENIG offers excellent corrosion resistance, flatness, and solderability. It is also suitable for fine-pitch components. However, ENIG can be relatively expensive compared to other surface finishes.
3. OSP (Organic Solderability Preservatives)
OSP is a surface finish that involves applying a thin layer of organic material to protect the copper traces. OSP provides a flat surface, excellent solderability, and is environmentally friendly. It is a cost-effective option and is suitable for both lead-free and leaded soldering processes. However, OSP is not as durable as other surface finishes and may require additional protection during assembly and handling.
4. Immersion Tin
Immersion tin, also known as white tin, is a surface finish that involves immersing the PCB in a solution of tin salts. It provides a flat surface, excellent solderability, and is cost-effective. Immersion tin is suitable for fine-pitch components and can withstand multiple reflow cycles. However, it is not recommended for applications with high-temperature or high-humidity environments.
5. Immersion Silver
Immersion silver is a surface finish that involves immersing the PCB in a solution of silver salts. It offers excellent solderability, planarity, and is cost-effective. Immersion silver is suitable for fine-pitch components and provides good electrical conductivity. However, it is prone to tarnishing and requires careful handling to prevent oxidation.
6. Lead Free Hot Air Surface Leveling(HASL)
This method resembles traditional HASL finishing but utilizes lead-free solder, making it eco-friendly and compliant with regulations like RoHS. It offers strong solderability and shields against oxidation.
7. Organic Surface Finishes
These finishes employ organic substances like carbon, gold, or silver to form a protective coating on the PCB. Examples include carbon ink, gold plating, and silver plating.
Suggested: GigaDevice: Empowering the Future with Innovative Solutions
Choosing the Right Surface Finish for Your PCB
Now that you are familiar with the different surface finish options, how do you choose the right one for your PCB? Here are some factors to consider:
1. Application Requirements
Consider the specific requirements of your application. Does it require high reliability, fine-pitch components, or resistance to harsh environments? Understanding the demands of your application will help you narrow down the surface finish options.
2. Cost
Cost is always a significant factor to consider in any PCB design. Evaluate the cost implications of each surface finish option and choose the one that fits within your budget without compromising the quality and reliability of your PCB.
3. Manufacturing Process
Consider the compatibility of the surface finish with your PCB manufacturing process. Some surface finishes may require additional steps or specialized equipment, which can impact the overall manufacturing timeline and cost.
4. Industry Standards
Check if there are any industry standards or customer requirements that dictate the choice of surface finish. Certain industries or applications may have specific surface finish requirements to ensure compliance and compatibility.
Conclusion
Choosing the right surface finish for your PCB is a critical decision that can impact the overall performance and reliability of your electronic product. Evaluate the different options based on your application requirements, cost considerations, manufacturing process, and industry standards. By making an informed choice, you can ensure that your PCB meets the necessary specifications and performs optimally in its intended application.