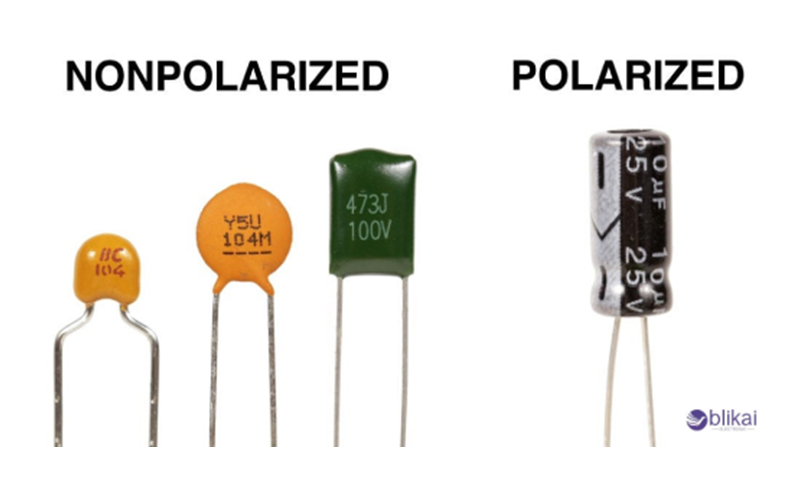
Understanding Polarized and Non-Polarized Capacitors
What are Polarized Capacitors?
Polarized capacitors are electrical devices whose operation indeed is subject to polarization.
One terminal is to be given positive voltage, the other terminal negative voltage. These capacitors are usually marked with a positive (+) sign on one terminal and negative on the other terminal.
In most polarized capacitors, anodes and cathodes are connected by a dielectric material between them (called the anode-cathode design). An electrolyte solution or polymer film serves as the dielectric layer of this type of capacitor, which uses metals or metal oxides as electrodes. In applications requiring high capacitance, it is extremely useful since it can store a lot of charge.
Most polarized capacitors use a solid dielectric material between electrodes (commonly called the anode-cathode design). They protect sensitive electrical equipment from damage due to electrostatic discharge. Proper installation is critical to achieving the satisfactory performance of polarized capacitor circuits because otherwise they may destroy other components. Always double-check your installation when working with polarized capacitors.
What are Non Polarized Capacitors?
Electrochemical components that store energy as electric fields are non-polarized capacitors. Ceramic, paper, plastic film, air, or vacuum separates two conductive plates.
In AC circuits, non-polarized capacitors can reduce power consumption and filter noise. In electronic applications, they are ideal because they can carry current in either direction. The polarity of non-polarized capacitors is not specified like that of polarized capacitors. Because of this, they can be connected both positively and negatively.
Compared with polarized capacitors, they also offer a wider range of capacitance values and are more tolerant of temperature variations. In high power circuits, non-polarized capacitors can be used since they are rated for higher voltage. Many DC applications use them, such as power supplies and motor control circuits. In audio gear, they are also used for filtering noise from signals. Since non-polarized capacitors are versatile and are available in a wide range of sizes and tolerance levels, they are an ideal solution for many electronic applications.
Polarized vs Non-Polarized Capacitor: Differences
Let’s dig into the difference between non polarized and polarized capacitors now that you know the basics.
Structure
The point discharge of an electronic device does not affect the use of any capacitor, regardless of its shape. It is rare to find an electrolytic capacitor in a square shape. A capacitor may be cylindrical, square, combined square, or tubular. It is important in high-frequency and intermediate-frequency devices not to disregard the invisible distributed capacitors.
Different Dielectric
Compared to other capacitors that have the same volume, polarity capacitors have a larger capacitance since they use electrolytes as a dielectric. Polarity capacitors will have different capacitances due to different electrolyte materials and processes. Dielectric materials are primarily responsible for voltage resistance. The nature of the dielectric determines whether polarity or non-polarized capacitors should be used, including metal oxide film and polyester.
Frequencies
There is a higher frequency of operation with non-polarized capacitors. In audio equipment and motor control circuits, they can filter signal noise or serve as signal noise filters. The lower frequencies of polarized capacitors make them unsuitable for these uses.
Capacity
A polarized capacitor, however, offers a much greater capacity, meaning it can store more charge than a non-polarized one. In applications such as voltage regulators and power supplies, they are ideal for applications requiring high capacitance.
Can We Use a Non-Polarized Capacitor Instead of Polarized?
Non-polarized capacitors can be used instead of polarized ones. A non-polarized capacitor is a superset of a polarized capacitor. Ceramics do not exhibit polarization issues when replacing electrolytics. Capacitors with equal capacitance and voltage ratings can generally replace polarized capacitors. The only time you should replace non-polarized capacitors with non-polarized capacitors is if you are certain the circuit will always apply voltage in one polarity.
A polarized capacitor would be preferred over a non polarized capacitor in low-frequency applications.
Do I Need a Polarized Capacitor?
Power supplies (storage) are filtered with polarized capacitors. When the amplifier stages are coupled together, they prevent DC from forming. Their small, cost-effective packages offer massive capacitance values. Compared to polarized caps of similar capacitance and voltage, non-polarized caps tend to be less expensive when they are fabricated from polarized material.
Final Thoughts
In capacitors, polarization refers to what has a certain positive or negative polarity. An unpolarized capacitor is one that is neither positive nor negative, meaning that it is not polarized. Thus, performance, capacity, structure, and environment differ between them.
Polarized vs non-polarized capacitors are discussed in this article. Hopefully, you now understand the uses and advantages of each type of electronic component. It is ultimately up to you to decide whether to use polarized or non-polarized capacitors. So if you still have any confusion, let me know in the comment section. Thank You!








