Understanding LED Drivers: Ensuring Efficiency and Longevity in LED Lighting
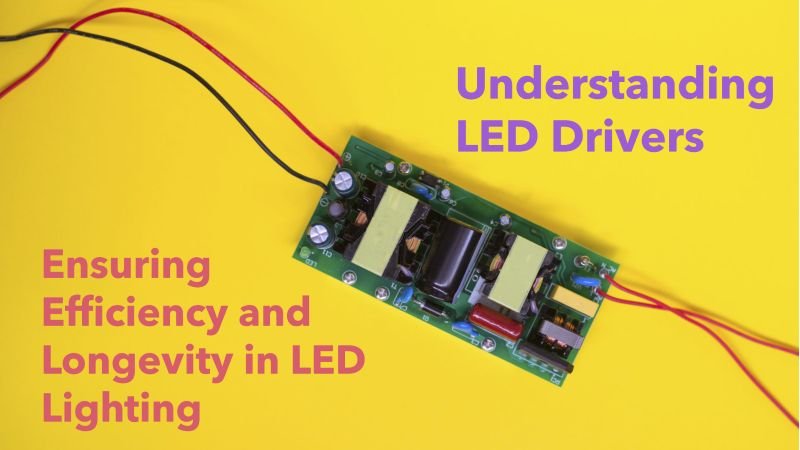
LEDs, or Light Emitting Diodes, have revolutionized the lighting industry with their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and eco-friendly nature. However, these advanced lighting solutions require a crucial component to function properly: the LED driver. Often described as the heart of an LED system, an LED driver ensures that LEDs operate efficiently and reliably, making it a cornerstone of modern lighting technology.
What is an LED Driver?
An LED driver is an electrical device that regulates and supplies the appropriate amount of current and voltage to an LED or an array of LEDs. Since LEDs are highly sensitive to fluctuations in power, the driver’s role is to ensure stable and consistent operation.
The primary purpose of an LED driver is to:
- Deliver a steady current or voltage, depending on the LED’s requirements.
- Protect the LED from power surges, voltage spikes, and other electrical irregularities.
- Extend the lifespan of the LED by maintaining optimal operating conditions.
By fulfilling these roles, an LED driver ensures that LEDs achieve their promised performance and longevity.
Why Do LEDs Need a Driver?
LEDs are semiconductor devices that emit light when current flows through them. Unlike traditional light bulbs, LEDs do not operate directly on standard power supplies. They:
- Require precise current control: LEDs are highly sensitive to overcurrent, which can damage them.
- Operate within a narrow voltage range: Small fluctuations can cause significant performance issues or shorten their lifespan.
How LED Drivers Help
LED drivers address these challenges by:
- Regulating the electrical input to match the LED’s requirements.
- Protecting against issues such as overvoltage, overcurrent, and thermal fluctuations.
- Enhancing efficiency by optimizing power delivery, ensuring the LED operates at its peak performance without wasting energy.
Without an LED driver, the reliability and longevity of LEDs would be compromised, negating many of their inherent advantages.
Types of LED Drivers
Constant Current Drivers
Constant current drivers supply a fixed current to the LED while allowing the voltage to vary within a specified range. These drivers are commonly used for applications where maintaining consistent brightness is critical, such as:
- Architectural lighting.
- Stage and studio lighting.
- Industrial LED systems.
Advantages:
- Prevents thermal runaway by maintaining a steady current.
- Ensures uniform brightness across multiple LEDs in series.
Constant Voltage Drivers
Constant voltage drivers deliver a fixed voltage while allowing the current to adjust based on the LED’s requirements. These drivers are suitable for:
- LED strips.
- Signage and displays.
- Decorative lighting installations.
Advantages:
- Simplifies wiring in parallel LED configurations.
- Ideal for systems where the voltage drop across LEDs is predictable.
Comparison: Constant Current vs. Constant Voltage
| Feature | Constant Current | Constant Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| Regulation Type | Fixed current, variable voltage | Fixed voltage, variable current |
| Best For | Series LED configurations | Parallel LED configurations |
| Key Benefit | Prevents overheating and ensures consistent brightness | Simplifies installation and compatibility with LED strips |
Components of an LED Driver
Key Internal Components
- Transformer:
- Converts high input voltage to a level suitable for LEDs.
- Provides isolation between the input and output circuits for safety.
- Controller:
- Manages the regulation of current and voltage.
- Enables dimming and other advanced functionalities in modern LED drivers.
- Capacitors:
- Smooth out voltage fluctuations and reduce noise in the power supply.
- Help maintain stable operation under varying load conditions.
- Protective Components:
- Include elements like fuses, surge suppressors, and thermal cutoffs.
- Safeguard the LEDs and the driver itself from damage due to electrical faults.
Role in Power Delivery and Protection
Each component works together to:
- Deliver power efficiently and reliably.
- Protect the LED system from environmental and electrical stress.
- Enable additional features like dimming, smart controls, and energy-saving modes.
By integrating these components, an LED driver acts as both a power manager and a safeguard, ensuring that LEDs operate smoothly in diverse applications.
Features of a Good LED Driver
Reliability and Efficiency
A good LED driver ensures consistent performance under various operating conditions. High-quality drivers are energy-efficient, converting most of the input power into usable energy for the LEDs, with minimal loss as heat.
Dimming Capability
Modern LED drivers support dimming, allowing users to adjust brightness levels. Dimmable drivers can work with:
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) dimming.
- Analog dimming methods. This feature enhances energy savings and provides greater control over lighting ambiance.
Over-Voltage, Over-Current, and Thermal Protection
A reliable driver includes safety mechanisms to protect against electrical and thermal stress. These safeguards prevent damage to the LED and ensure long-term reliability by addressing issues such as:
- Voltage surges.
- Excessive current flow.
- Overheating due to environmental or operational factors.
Compatibility with Smart Lighting Systems
Advanced LED drivers are designed to integrate seamlessly with smart home and building systems. Features like wireless connectivity, remote control, and programmability make them ideal for IoT-enabled lighting solutions.
Applications of LED Drivers
Here are some common applications of LED Drivers:
Indoor and Outdoor Lighting
LED drivers are used in a wide range of lighting applications:
- Residential: Energy-efficient lighting for homes, including dimmable fixtures and LED strips.
- Commercial: High-performance lighting for offices, retail spaces, and warehouses.
- Outdoor: Streetlights, floodlights, and garden lighting systems that require waterproof and weather-resistant drivers.
Automotive Lighting
LED drivers power various automotive lighting solutions, such as:
- Headlights and taillights.
- Interior lighting.
- Specialty applications like ambient lighting systems.
Specialized Applications
In specialized fields, LED drivers are crucial for:
- Displays and digital signage.
- Backlighting for screens.
- Medical and industrial lighting solutions requiring precise performance.
Selecting the Right LED Driver
Factors to Consider
- Power Requirements:
- Match the driver’s output power to the LED’s specifications (e.g., voltage and current).
- Type of LED:
- Single or multiple LEDs, high-power or low-power LEDs, and series vs. parallel configurations.
- Environmental Conditions:
- Consider factors like temperature, humidity, and exposure to water or dust. Use IP-rated drivers for outdoor and harsh environments.
Importance of Matching the Driver to LED Specifications
Using an incompatible driver can lead to issues like flickering, overheating, or reduced LED lifespan. Ensuring compatibility is key to achieving optimal performance and longevity.
Advancements in LED Driver Technology
Recent innovations in LED driver technology have introduced features such as:
- Smart Drivers: Programmable and IoT-enabled drivers that allow remote monitoring and control.
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Designs that minimize energy loss and heat generation.
- Compact Designs: Smaller drivers suitable for space-constrained applications.
- Dynamic Controls: Support for color tuning, adaptive dimming, and integration with advanced lighting systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, LED drivers plays a imp role in ensuring the performance, safety, and longevity of LED lighting systems. By regulating power supply and protecting against electrical irregularities, they allow LEDs to operate at their full potential. When selecting an LED driver, it is essential to consider factors like power requirements, environmental conditions, and compatibility with smart systems. As LED technology continues to evolve, advancements in driver design will further enhance the capabilities and applications of LED lighting.